Today, I will break down a somewhat technical but crucial search engine optimization (SEO) aspect: Google’s heading vectors. While the term may sound intimidating, understanding how they function can significantly impact your website’s search rankings. When utilized correctly, heading vectors are powerful tools that help search engines better interpret your content, giving your pages an advantage in search results. You can LISTEN to a conversation about the patent below or DOWNLOAD it at the bottom of the article.
What Are Google’s Heading Vectors?
At its core, Google’s patent on heading vectors, formally known as “Context scoring adjustments for answer passages,” involves using a sophisticated method to analyze headings on web pages. The goal is to improve search engine results by understanding the structure and context of the content. Essentially, Google looks at heading tags (H1 to H6) as road signs that guide its algorithms through web page sections. This helps Google assess the topical relevance and hierarchy of content.
The vectors in question refer to the mathematical modeling of these headings, where the content under each heading is analyzed for thematic relevance. This means that Google doesn’t just look at the heading itself but also considers the following content’s depth, breadth, and alignment. Understanding these aspects allows website owners to optimize the user experience and make it easier for search engines to identify valuable information.
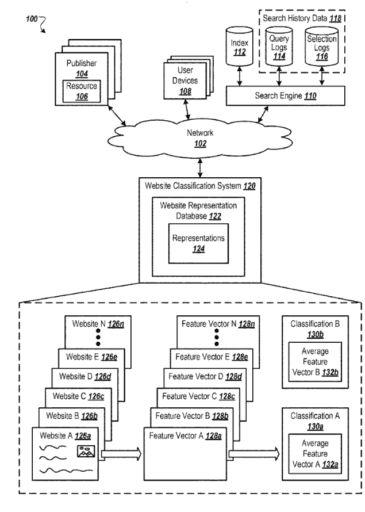
This approach is further supported by Google’s patent application for “Website Representation Vectors,” which describes how data from various websites generate composite representations, helping classify new websites based on their similarity to previously analyzed ones. This system allows Google to refine its understanding of a website’s structure, mainly through elements like headings, to enhance the accuracy of search results.
How Do Heading Vectors Impact SEO?
- Header Tags Are Key: Header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) are not just about styling; they help structure your content in a way that Google can understand. The H1 tag, usually the main title, signals the page’s primary focus. Subheadings like H2, H3, and so on provide a clear hierarchy. When used appropriately, these tags form a roadmap that guides users and search engine bots. A well-structured page with properly used heading tags can help improve search visibility, as Google can more easily identify which content is crucial and which is supplementary.
- Size and Style Matter: The visual presentation of headings, such as size, weight, and font style, also sends signals to Google. Larger and bolder headings naturally draw a reader’s attention, suggesting importance. While using oversized or bold headings everywhere to emphasize content is tempting, overdoing it can detract from user experience. A cluttered page may confuse visitors, indirectly affecting metrics like dwell time and bounce rate—factors that impact SEO.
- Keywords Still Count: Using relevant keywords within headings is still an essential practice in SEO. When your headings incorporate keywords that genuinely reflect the section’s content, it helps Google match your page to related search queries. However, excessive keyword usage, known as keyword stuffing, is counterproductive. Instead of boosting rankings, it can lead to penalties, so keep your keyword usage natural and focused.
- User Experience is King: Beyond satisfying algorithms, Google’s primary goal is to provide a valuable user experience. Clear and descriptive headings allow visitors to scan your content and locate the necessary information. When users can easily navigate your page, they’re more likely to stay longer, reducing the bounce rate—a signal that Google interprets as a sign of quality. The longer people stay engaged with your content, the more Google views your page as authoritative and useful.
The Role of Context in Heading Vectors
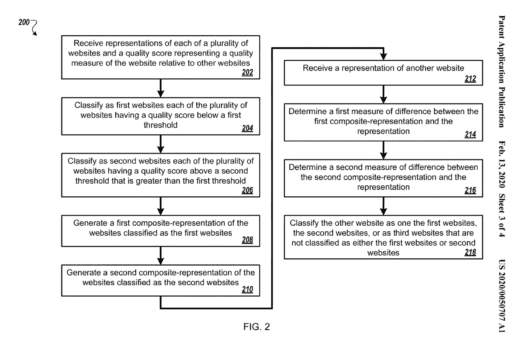
Google’s heading vectors go beyond just recognizing the text within header tags. They also assess the context around each heading to determine whether the content delivers the title’s promise. Suppose a heading signals a specific topic or question, but the following content doesn’t provide a satisfactory answer or relevant information. In that case, Google may down-rank that section or the entire page. Therefore, creating content that aligns well with each heading is essential.
For example, an H2 heading titled “Benefits of Organic SEO” should be followed by content that thoroughly covers the advantages of organic SEO. If this section starts talking about paid search instead, it will confuse both users and search engines, potentially harming the page’s rankings. The idea is to create a consistent and logical flow of information.
Best Practices for Using Heading Vectors
To maximize the benefits of heading vectors for SEO, consider these best practices:
- Use Headings Strategically: Treat headings as signposts for search engines and human readers. Use them to break down long content into smaller, more digestible sections. Avoid placing headings arbitrarily or excessively, as this can disrupt the logical structure of your content. Each heading should represent a new topic or subtopic that builds upon the previous one.
- Keep Headings Descriptive: Vague or clickbait-style headings may attract initial clicks but can lead to high bounce rates if the content fails to meet expectations. Instead, ensure each heading accurately describes the section it introduces. Descriptive headings improve content discoverability and help Google’s algorithms better categorize your page.
- Every Heading Should Be Unique: Avoid repeating the same heading across different page sections. Unique headings prevent confusion for both users and search engines. Repetitive headings may signal a lack of depth in your content, making it harder for Google to differentiate between sections.
- Follow the Hierarchical Structure: Headings should follow a logical order, starting with H1 for the main title, then H2 for primary subheadings, and subsequently H3 for sub-sections within the H2 topic. Consistent hierarchy helps Google understand the relationships between different sections of content.
- Keywords Matter, But Don’t Overdo It: While it’s essential to include keywords in your headings, overusing them or forcing them where they don’t fit can harm the readability and user experience. Focus on natural language and contextually relevant keywords that align with the user’s intent. Think about the questions your audience may ask and create headings that provide clear answers.
- Use Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) Keywords: Alongside your main keywords, incorporate LSI keywords—terms and phrases related to the primary keyword. For instance, if your heading is about “SEO Best Practices,” using related terms like “search engine optimization tips” or “improving website visibility” in the subheadings adds depth to your content.
- Regularly Update Content to Reflect Changing Trends: SEO is not static, and what may work today might not be as effective tomorrow. Revisiting and updating your headings to reflect current industry trends or changes in user search behavior can help maintain your content’s relevance.
How Heading Vectors Fit Into a Broader SEO Strategy
Heading vectors are just one part of the SEO puzzle. While they can significantly improve how Google perceives your content, other factors also affect overall website performance. These include:
- On-page SEO Elements: Meta descriptions, alt text for images, internal links, and keyword optimization are still fundamental.
- Content Quality: Google will always prioritize high-quality, informative content. Heading vectors help, but users will leave if the content doesn’t provide value, signaling low quality.
- Technical SEO: Ensuring fast page load times, mobile optimization, and clean URL structures provides a seamless user experience.
- Backlink Profile: Quality backlinks from reputable sites improve domain authority and signal credibility.
Integrating heading vector optimization with these broader SEO practices will create a more robust and effective SEO strategy.
Conclusion
Google’s heading vectors are an advanced approach to understanding web content but boil down to basic principles: organization, clarity, and relevance. Properly using heading tags helps both users and search engines navigate your content. By implementing best practices like following a logical heading structure, using descriptive and unique headings, and naturally incorporating keywords, you can make the most of heading vectors to enhance your SEO performance.
Remember, SEO is about creating a great user experience. When your content is easy to navigate and meets user intent, people and algorithms will appreciate it. So, start optimizing your headings today to help guide Google—and your audience—through your content in the most meaningful way possible.